Today we will discuss about welding and types of welding.
Welding is a process of joining similar and dissimilar metals or other material by application of heat with or
without application of pressure and addition of filler material. It is used as
permanent fasteners. Welding is essential process of every manufacturing industries. In fact, the future of any new metal may
depend on how far it would lend itself to fabrication by welding.
The weldability has been defined as the capacity of being
welded into inseparable joints having specified properties such as definite
weld strength proper structure. The weldability of any metal depends on five
major factors. These are melting point, thermal conductivity, thermal
expansion, surface condition, and change in microstructure.
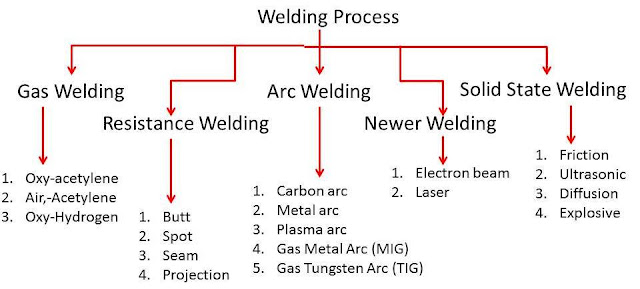
Types of welding:
1. Plastic welding:
In plastic welding or pressure welding process, the pieces of
metal to be joined are heated to a plastic state and then forced together by
external pressure. These welding are also known as liquid-solid welding process. This procedure is used in forge welding and resistance welding.
2. Fusion welding:
In the fusion welding or no pressure welding process, the material
at the joint is heated to a molten state and allowed to solidify. These welding are also known as liquid state welding process. This includes
gas welding, arc welding, thermite welding etc.
3. Cold welding:
In this welding process, the joints are produced without application of heat, but by applying pressure which results diffusion or inter-surface
molecular fusion of the parts to be joined. It is also known as solid state welding process. This process is mainly used for
welding nonferrous sheet metal, particularly aluminum and its alloys. This includes ultrasonic welding, friction welding, Explosive welding etc.
4 Main Welding Processes:
1. Arc Welding (Fusion Welding):
In this type of welding process, weld metal melted from the edges to
be joined and allow to solidifies from the liquid state and usually below the
recrystallization temperature without any applied deformation. Arc welding is most extensively employed
method of joining metal parts by fusion. In this welding the arc column is
generated between an anode, which is the positive pole of power supply, and the
cathode, the negative pole. When these two conductors of an electric circuit
are brought together and separated for a small distance such that the current
continues to flow through a path of ionized particles called plasma, an electric
arc is formed. This ionized gas column acts as a high resistance conductor that
enables more ions to flow from the anode to the cathode. Heat is generated as
the ions strike the cathode. This heat used as melting of metal to be joined or
melting the filler metal which further used as joining material of welding
metal. The electrode is either consumable or non-consumable as per welding
requirement. The temperature at the
center of the arc being 6000 OC to 7000OC
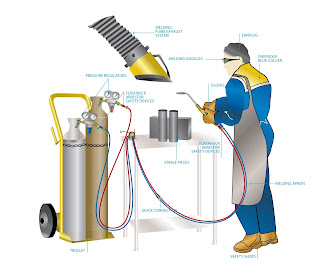
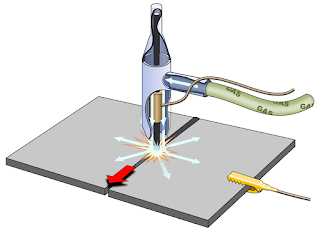
2. Gas Welding:
The gas welding is done by burning of combustible gas with
air or oxygen in a concentrated flame of high temperature. As with other welding
methods, the purpose of the flame is to heat and melt the parent metal and
filler rod of a joint. It can weld most common materials
3. Gas Metal arc welding (MIG):
This welding is also known as metal inert gas welding. In this
type of welding a metal rod is used as one electrode, while the work being
welded is used as another electrode. It is a gas shielded metal arc welding
which uses the high heat of an electric arc between a continuously fed,
consumable electrode wire and the material to be welded. Metal is transferred
through protected arc column to the work.
In this process the wire is fed continuously from a reel
through a gun to constant surface imparts a current upon the wire. In this
welding the welding area is flooded with a gas which will not combine with the
metal. The rate of flow gas is sufficient to keep the oxygen of the air away
from the hot metal surface while welding is being done.
Also Read : Difference between Mig and Tig Welding
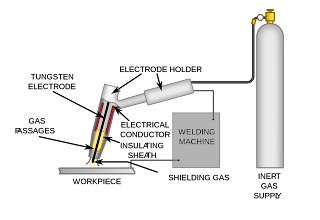
4. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (TIG):
This welding is also known as tungsten inert gas welding is
similar to the MIG in that is uses the gases for shielding. This arc welding process
uses the intense heat of an electric arc between a no consumable tungsten
electrode and the material to be welded. In this process the electrode is not consumable
during welding process and gas is used to protect the weld area form
atmospheric air.
Today We have discussed about welding and Types of Welding. If you have any doubt or query put it in comment box.